The Role of Biometric Technology in Enhancing Security and Privacy. In a world increasingly reliant on digital interactions, ensuring security and privacy has become paramount. Biometric technology offers a powerful solution, leveraging unique physiological and behavioral traits such as fingerprints, facial patterns, and voice recognition to verify identity. This article explores the applications of biometric technology, its potential to enhance security, and the ethical considerations that come with its widespread use.
What Is Biometric Technology?
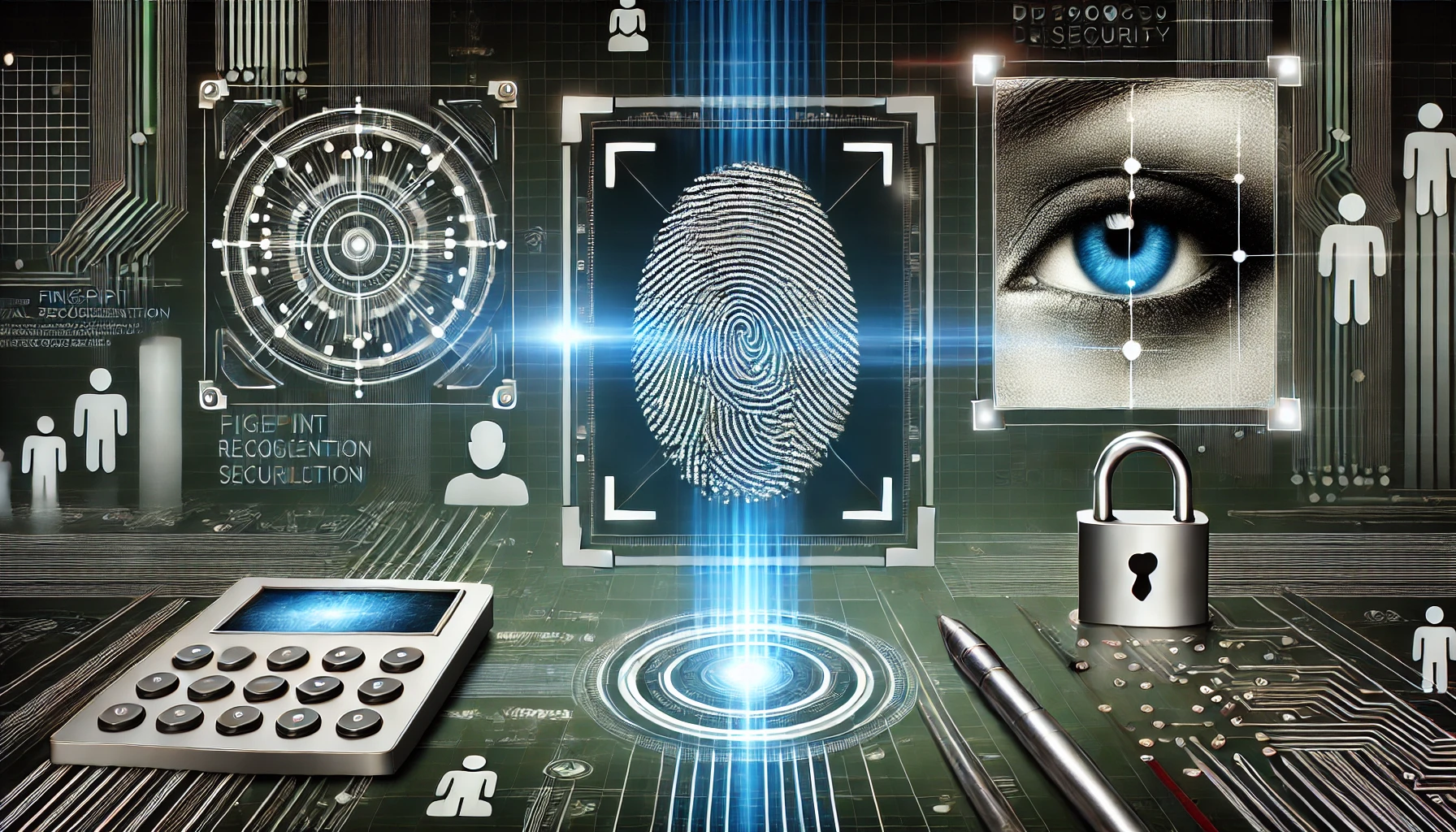
Biometric technology uses unique biological characteristics to authenticate identities. Unlike passwords or PINs, biometric data is difficult to replicate or steal, making it a robust alternative for securing personal and organizational information. Common biometric methods include:
- Fingerprint Recognition: Scanning fingerprints to grant access to devices, secure financial transactions, or log in to systems.
- Facial Recognition: Using unique facial features for identity verification, commonly seen in smartphones and surveillance systems.
- Voice Authentication: Identifying users through speech patterns for secure communication and access control.
- Iris and Retina Scanning: Analyzing unique eye patterns for high-security applications.
Applications of Biometric Technology
1. Strengthening Digital Security
Biometric technology significantly reduces reliance on traditional passwords, which are prone to being forgotten, reused, or hacked. By requiring unique biological traits, it ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data. For instance, fingerprint scanners on smartphones provide an additional layer of security for mobile banking apps, reducing the risk of fraud.
Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA), which combines biometrics with other verification methods, further strengthens security frameworks. This approach is increasingly common in industries like finance, where protecting sensitive data is critical. For tips on maintaining cybersecurity in today’s digital world, explore 10 Must-Know Cybersecurity Tips to Stay Safe.
2. Enhancing Access Control
Organizations are deploying biometric systems to improve access control in workplaces and secure areas. For example, biometric entry points in offices or research facilities prevent unauthorized individuals from entering. Advanced systems can integrate facial recognition with employee databases, automating attendance tracking and streamlining HR operations.
Public venues, such as airports, also benefit from biometric technology. Automated passport control systems use facial recognition to match travelers to their identification documents, expediting border crossings and enhancing security.
3. Revolutionizing Financial Transactions
Biometrics are transforming how financial transactions are conducted. Fingerprint and facial recognition are now common for authorizing payments on mobile devices, providing a seamless and secure experience. Voice authentication is gaining popularity for customer service interactions, enabling secure account management without the need for complex passwords.
Biometric-based digital wallets are poised to redefine e-commerce, ensuring transactions remain secure while enhancing user convenience. This evolution aligns with the broader trend of integrating innovative technologies into finance, as discussed in How Blockchain Is Redefining Digital Identity.
4. Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, biometric technology streamlines patient identification, ensuring accurate medical records and personalized treatment. Iris scanning and facial recognition are being integrated into hospital systems to prevent identity mix-ups and enhance patient safety. Biometrics also facilitate secure access to electronic health records (EHRs), protecting sensitive medical data from breaches.
For telemedicine, voice recognition allows physicians to authenticate themselves during remote consultations, safeguarding patient privacy while enabling efficient care delivery.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
While biometric technology offers numerous benefits, it raises important ethical questions. The collection and storage of sensitive biometric data present significant privacy risks. If compromised, such data cannot be changed like passwords, leaving individuals vulnerable to identity theft.
Furthermore, concerns about surveillance and misuse are growing. Facial recognition technology, for instance, has faced criticism for its potential to infringe on personal freedoms when used in public spaces without consent. Addressing these challenges requires transparent policies, robust data protection measures, and clear guidelines on the ethical use of biometric systems.
The Future of Biometric Technology
The future of biometrics lies in continuous innovation and ethical implementation. Emerging trends include:
- Behavioral Biometrics: Monitoring unique behaviors, such as typing speed and navigation patterns, to enhance authentication processes.
- AI Integration: Leveraging artificial intelligence to improve accuracy and adaptability in biometric systems.
- Decentralized Storage: Using blockchain technology to securely store biometric data, minimizing centralized vulnerabilities.
As biometric technology advances, its applications will expand into new domains, further intertwining security and convenience. However, ensuring ethical usage and robust privacy protection will remain critical to its success.
Conclusion
Biometric technology is redefining security and privacy across industries, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges. From securing financial transactions to revolutionizing healthcare and access control, its impact is undeniable. However, as we embrace these advancements, it is essential to address ethical concerns and prioritize data protection.
For more on balancing innovation and ethics, explore The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence and Its Balance.




Leave a Reply